Starting a new business is an exciting venture, but securing funding can be a daunting task. One of the most common ways to finance a new business is through a commercial loan, but qualifying for one can be tricky. Lenders want to see a solid business plan, a good credit history, and a clear understanding of your financial obligations.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate the process of obtaining a commercial loan for your new business.
From understanding the different types of loans available to building a strong business plan and establishing creditworthiness, we’ll cover all the essential steps to help you increase your chances of getting approved. We’ll also discuss crucial factors like choosing the right lender, negotiating favorable loan terms, and managing loan repayment effectively. Let’s dive in and explore the path to securing the financial resources you need to launch your business successfully.
Understanding Commercial Loans

Securing financing for your new business can be a daunting task, but understanding the different types of commercial loans available can help you navigate the process. Commercial loans are designed to help businesses acquire necessary funds for various purposes, from purchasing equipment to expanding operations.
Types of Commercial Loans
Commercial loans come in various forms, each tailored to specific business needs and financial situations. The most common types include:
- Term Loans: Term loans are a fixed amount of money borrowed for a specific period with a fixed interest rate. They offer predictable monthly payments and are often used for long-term investments, such as purchasing equipment or real estate.
- Lines of Credit: Lines of credit provide a flexible funding option, allowing businesses to borrow funds as needed up to a pre-approved limit. Interest is charged only on the amount borrowed, making them suitable for short-term working capital needs.
- Equipment Financing: Equipment financing specifically targets the purchase of machinery, vehicles, or other essential equipment. These loans are often secured by the equipment itself, providing lenders with collateral.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) Loans: Backed by the U.S. Small Business Administration, SBA loans offer favorable terms and lower interest rates for small businesses. They are particularly beneficial for startups and businesses with limited credit history.
- Invoice Financing: Invoice financing provides funding based on the value of outstanding invoices. This option helps businesses accelerate cash flow by receiving immediate payment for their invoices, even before customers make full payment.
Key Features and Benefits
Each type of commercial loan comes with unique features and benefits that cater to different business needs.
- Term Loans: Term loans offer predictable monthly payments, making budgeting easier. They also provide a fixed interest rate, ensuring stability in loan costs.
- Lines of Credit: Lines of credit provide flexibility, allowing businesses to borrow funds only when needed. They also offer the advantage of lower interest costs compared to term loans, as interest is only charged on the borrowed amount.
- Equipment Financing: Equipment financing simplifies the purchase of essential equipment by providing dedicated funding for this specific purpose. It also often offers lower interest rates than other loan types.
- SBA Loans: SBA loans offer favorable terms, including lower interest rates and longer repayment periods. They also require less stringent credit requirements, making them accessible to businesses with limited credit history.
- Invoice Financing: Invoice financing helps businesses overcome cash flow challenges by providing immediate access to funds based on outstanding invoices. This can significantly improve a business’s financial stability and ability to meet operational expenses.
Comparing Interest Rates, Terms, and Eligibility Requirements
The interest rates, terms, and eligibility requirements for commercial loans vary significantly depending on the lender, the type of loan, and the borrower’s financial situation.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate | Terms | Eligibility Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Term Loan | Fixed, typically higher than other loan types | 1-25 years | Good credit history, strong financial statements, collateral may be required |
| Line of Credit | Variable, typically lower than term loans | 1-10 years | Good credit history, strong financial statements, may require collateral |
| Equipment Financing | Variable, often lower than other loan types | 1-10 years | Good credit history, strong financial statements, equipment serves as collateral |
| SBA Loan | Variable, typically lower than conventional loans | 10-25 years | Good credit history, strong business plan, may require collateral |
| Invoice Financing | Variable, based on invoice value | Short-term, typically 30-90 days | Good credit history, strong customer base, healthy invoice volume |
Remember: It’s crucial to compare different loan options and lenders before making a decision. Consider factors such as interest rates, terms, fees, and eligibility requirements to find the loan that best suits your business needs.
Building a Strong Business Plan
A comprehensive business plan is essential for securing a commercial loan. It serves as a roadmap for your business, outlining your vision, strategies, and financial projections. A well-structured business plan demonstrates your understanding of the market, your business model, and your ability to generate revenue and manage finances. It’s your opportunity to showcase the potential of your business and build confidence in lenders.
Demonstrating Viability and Profitability
A solid business plan should clearly articulate the viability and profitability of your business. Lenders want to see a business with a strong foundation and a clear path to success.
- Market Analysis: Provide a thorough analysis of your target market, including market size, growth potential, and competitive landscape. Identify your unique selling proposition (USP) and how you differentiate yourself from competitors.
- Business Model: Clearly describe your business model, including your products or services, pricing strategy, and distribution channels. Explain how you will generate revenue and achieve profitability.
- Management Team: Highlight the experience, expertise, and track record of your management team. Lenders want to see a team with the skills and knowledge to navigate the challenges of running a successful business.
Financial Projections
A compelling financial forecast is crucial for securing a loan. It provides lenders with a clear picture of your business’s financial health and its potential for generating returns.
- Revenue Projections: Provide realistic and well-supported revenue projections based on market research, industry trends, and your own sales forecasts. Explain your assumptions and how you arrived at your estimates. For example, a restaurant may project revenue based on average customer spending, projected foot traffic, and anticipated table turnover rate.
- Expense Projections: Detail your projected expenses, including operating costs, marketing expenses, salaries, and rent. Be specific and realistic in your estimates. For example, a technology startup might project expenses based on software development costs, marketing campaign budgets, and anticipated employee salaries.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Include a detailed cash flow analysis, which shows the movement of cash in and out of your business over time. This helps lenders understand your ability to manage cash flow and meet your financial obligations. For example, a retail business might analyze cash flow based on seasonal sales patterns, inventory levels, and accounts receivable collection periods.
Important Considerations
- Financial Statements: Include historical financial statements if available. This provides lenders with a baseline understanding of your business’s financial performance. If you are a new business, you may need to provide personal financial statements to demonstrate your financial stability.
- Loan Request: Clearly state the amount of funding you are seeking and how you intend to use the loan. Be specific about the loan purpose and how it will contribute to your business’s growth and profitability.
- Loan Repayment Plan: Artikel a clear and realistic plan for repaying the loan. This includes a repayment schedule, interest rates, and any collateral you are offering. Lenders want to see that you have a solid understanding of your financial obligations and a plan to meet them.
Gathering Required Documentation
Lenders need to evaluate your business’s financial health and potential before approving a loan. To do this, they require specific documentation to assess your creditworthiness and the viability of your business. Providing all necessary documentation promptly and accurately helps streamline the loan application process and increases your chances of approval.
Essential Documents for a Commercial Loan Application
- Business Plan: A well-written business plan is crucial. It Artikels your business’s mission, goals, target market, competitive analysis, marketing strategies, financial projections, and management team. This document demonstrates your understanding of your business and its future potential.
- Personal Financial Statements: Lenders need to assess your personal financial situation, especially if you are personally guaranteeing the loan. This includes your personal tax returns, bank statements, credit reports, and proof of assets.
- Business Tax Returns: These documents provide a detailed history of your business’s financial performance. They show revenue, expenses, profit or loss, and tax liabilities. Lenders use this information to assess your business’s profitability and tax compliance.
- Financial Statements: This includes your balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These documents provide a snapshot of your business’s financial position at a specific point in time.
- Business Licenses and Permits: These documents demonstrate that your business is operating legally and in compliance with all applicable regulations. Lenders need to ensure that your business is properly licensed and authorized to operate.
- Proof of Insurance: This includes general liability insurance, property insurance, and workers’ compensation insurance. This documentation shows that your business is adequately protected against potential risks, which reassures lenders.
- Collateral: If you are offering collateral to secure the loan, provide documentation of the collateral’s value and ownership. Collateral can include real estate, equipment, inventory, or accounts receivable.
- Bank Statements: These statements show your business’s cash flow and transaction history. Lenders use this information to assess your business’s financial stability and ability to repay the loan.
- Credit History: A strong credit history demonstrates your business’s ability to manage debt responsibly. Lenders may request a credit report from a business credit reporting agency, such as Dun & Bradstreet.
- Loan Application: Complete the loan application form provided by the lender, including information about your business, loan purpose, and repayment plan.
Choosing the Right Lender
Securing a commercial loan is a crucial step for any new business. Choosing the right lender can significantly impact your loan terms, interest rates, and overall experience. With so many options available, it’s essential to carefully evaluate your needs and compare different lenders before making a decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Lender
It’s important to consider several factors when selecting a commercial lender to ensure a smooth and beneficial lending experience.
- Reputation: Research the lender’s track record, financial stability, and customer reviews. Look for lenders with a strong reputation for fair practices and customer satisfaction.
- Loan Terms: Compare interest rates, loan terms, fees, and repayment options offered by different lenders. Choose a lender that provides terms that align with your business needs and financial capabilities.
- Customer Service: Assess the lender’s responsiveness, communication, and willingness to assist you throughout the loan process. Look for a lender with a dedicated team that is readily available to answer your questions and address your concerns.
- Flexibility: Consider the lender’s willingness to work with you on customized loan solutions. Some lenders may offer flexible terms, such as a grace period for repayment or the option to adjust your payment schedule if needed.
- Industry Expertise: Look for a lender that has experience working with businesses in your specific industry. They will have a better understanding of your unique challenges and opportunities.
Comparing Different Lending Institutions
There are various lending institutions available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Consider these options:
- Banks: Banks typically offer a wide range of loan products and services, including commercial loans. They often have strict lending criteria and may require a strong credit history and substantial collateral. However, banks can provide competitive interest rates and may offer additional financial services.
- Credit Unions: Credit unions are member-owned financial institutions that often offer more personalized service and lower interest rates than banks. They may have more flexible lending requirements and may be more willing to work with startups or businesses with limited credit history.
- Online Lenders: Online lenders are becoming increasingly popular for their convenience and faster loan processing times. They often offer flexible loan terms and may be more accessible to businesses with limited credit history. However, online lenders may have higher interest rates and may not offer the same level of personalized service as traditional lenders.
Resources for Finding Reputable Lenders
Several resources can help you find reputable and reliable commercial lenders:
- Small Business Administration (SBA): The SBA provides resources and guidance for small businesses, including a directory of SBA-approved lenders. These lenders are known for their commitment to supporting small businesses.
- Online Business Directories: Several online directories list commercial lenders, allowing you to compare their services and loan terms. Some popular directories include LendingTree, NerdWallet, and Bankrate.
- Industry Associations: Your industry association may have a list of recommended lenders that specialize in working with businesses in your sector.
- Networking: Reach out to other entrepreneurs and business owners for recommendations. They may have experience with different lenders and can offer valuable insights.
Negotiating Loan Terms
You’ve successfully built a solid business plan, gathered all the necessary documentation, and found a lender who’s interested in financing your business. Now comes the crucial step of negotiating the loan terms. This phase is where you ensure the loan works best for your business needs.
Understanding Key Loan Terms
Before diving into negotiations, you need to understand the key elements of a commercial loan agreement. These elements determine the financial obligations and risks associated with the loan.
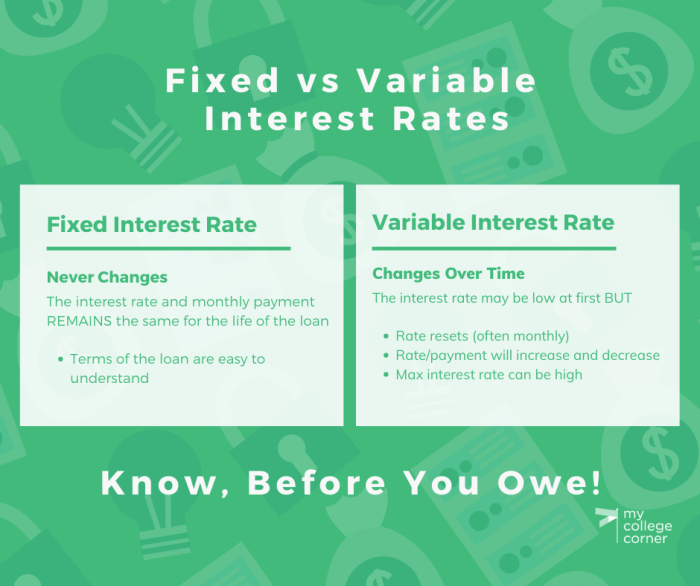
- Interest Rate: The cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the loan amount. The interest rate can be fixed, meaning it remains the same throughout the loan term, or variable, meaning it can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Repayment Terms: The schedule for repaying the loan, including the amount of each payment and the frequency of payments. Common repayment terms include monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- Collateral Requirements: Assets pledged as security for the loan. If you default on the loan, the lender can seize the collateral to recover their losses. Common types of collateral include real estate, equipment, and inventory.
Negotiating Favorable Terms
Negotiating favorable loan terms is essential for ensuring your business’s financial health. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Shop Around: Compare loan offers from multiple lenders to find the best interest rates, repayment terms, and collateral requirements. Don’t settle for the first offer you receive.
- Leverage Your Business Strengths: Highlight your business’s strengths, such as a strong track record, a solid management team, and a well-defined growth strategy. These factors can make you a more attractive borrower and potentially lead to better loan terms.
- Negotiate for Flexibility: If possible, try to negotiate flexible repayment terms, such as a longer loan term or a grace period on principal payments. This can provide you with more breathing room to manage your cash flow and navigate unexpected challenges.
- Explore Alternative Loan Structures: Consider alternative loan structures, such as lines of credit or equipment financing, which may offer more flexibility or lower interest rates than traditional term loans.
Understanding the Loan Agreement
Before signing any loan agreement, it’s crucial to carefully review the terms and conditions. Make sure you understand all the clauses, including:
- Prepayment Penalties: Fees charged if you pay off the loan early.
- Default Provisions: The consequences of failing to make loan payments, such as the lender’s right to seize collateral.
- Insurance Requirements: The types of insurance you must maintain, such as property insurance or business interruption insurance.
It’s essential to understand the terms of the loan agreement before signing. Seek legal advice if you have any questions or concerns.
Loan Approval Process
Once you’ve submitted your loan application and all the necessary documentation, the lender will begin the review process. This involves a thorough evaluation of your business, your financial history, and the loan request itself.
Credit Checks and Financial Analysis
The lender will conduct a comprehensive credit check to assess your personal and business creditworthiness. This involves examining your credit score, payment history, and outstanding debts. They will also analyze your financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, to understand your business’s financial health and ability to repay the loan.
Loan Underwriting
Loan underwriting is a critical step in the loan approval process. It involves a detailed assessment of the loan request and the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. Underwriters will consider various factors, including:
- Loan-to-value ratio (LTV): This ratio compares the amount of the loan to the value of the asset being financed. A higher LTV indicates a greater risk for the lender.
- Debt-to-equity ratio (D/E): This ratio measures the amount of debt a company has relative to its equity. A higher D/E ratio suggests a higher risk of financial distress.
- Debt service coverage ratio (DSCR): This ratio indicates the company’s ability to cover its debt payments with its operating income. A higher DSCR indicates a lower risk of default.
- Collateral: Lenders may require collateral, such as real estate or equipment, to secure the loan. This provides the lender with recourse if the borrower defaults.
- Industry outlook: The lender will also consider the overall health and outlook of the industry in which your business operates.
Loan Approval Timeline
The loan approval process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the loan request and the lender’s policies. Factors that can affect the timeline include:
- Loan amount: Larger loans typically require more extensive due diligence and underwriting, which can take longer.
- Loan type: Some loan types, such as SBA loans, involve additional government approvals and can take longer to process.
- Lender’s workload: If the lender is busy with other loan applications, the approval process may take longer.
- Completeness of documentation: Providing all the required documentation promptly can help expedite the process.
Loan Funding and Disbursement
Once your commercial loan application is approved, the lender will initiate the process of funding and disbursing the loan amount. This involves a series of steps to ensure the funds are released safely and efficiently. The disbursement process involves transferring the approved loan amount to your business account, allowing you to access the funds for your business operations.
Loan Disbursement Methods
The method of disbursing loan funds varies depending on the lender and the loan type. Common disbursement methods include:
- Wire Transfer: This is the most common method, where funds are electronically transferred directly to your business bank account. It’s typically a secure and efficient way to receive loan funds.
- Check: Some lenders may issue a check, which can be deposited into your business account. This method is less common due to the risk of loss or theft.
- Direct Deposit: This method allows the lender to deposit the funds directly into your business account, similar to a payroll deposit.
Loan Disbursement Timelines
The time it takes for loan funds to be disbursed can vary depending on the lender and the complexity of the loan. Typically, it can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks.
- Simple Loans: For loans with straightforward documentation and approval processes, disbursement can occur within a few days.
- Complex Loans: Loans requiring extensive due diligence, legal documentation, or multiple parties involved may take longer, potentially weeks, to be disbursed.
Managing Loan Funds Effectively
Once you receive the loan funds, it’s crucial to manage them effectively to ensure you maximize the benefits and avoid unnecessary debt.
- Develop a Budget: Create a detailed budget outlining how you plan to utilize the loan funds. This will help you track your spending and ensure you’re using the money for its intended purpose.
- Prioritize Expenses: Focus on using the funds for essential business needs, such as inventory, equipment, or marketing, that will contribute to your long-term growth and profitability.
- Track Loan Payments: Keep meticulous records of your loan payments, interest rates, and any associated fees. This will help you stay organized and avoid any late payment penalties.
Understanding Loan Risks and Responsibilities
Securing a commercial loan is a crucial step for any new business, but it’s essential to understand the inherent risks involved. While a loan can provide the financial boost you need to launch or expand your operations, it also comes with financial obligations and potential challenges.
Understanding Loan Risks
The potential risks associated with commercial loans can be categorized into three primary areas:
- Default: The most significant risk is the possibility of defaulting on your loan. This occurs when you fail to make timely payments on your loan as per the agreed-upon terms. Defaulting can have severe consequences, including:
- Damage to Credit Score: A default significantly impacts your business’s credit score, making it challenging to secure future loans or financing.
- Legal Action: Lenders may pursue legal action to recover the outstanding debt, which could result in asset seizure or even personal liability for the business owner.
- Loss of Business: Defaulting on a loan can lead to financial instability and, in severe cases, even business closure.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Interest rates can fluctuate over time, impacting your loan payments. A rise in interest rates can lead to higher monthly payments, potentially straining your cash flow and impacting your business’s profitability.
- Variable Interest Rates: Variable interest rates are tied to a benchmark rate, such as the prime rate or LIBOR. These rates can fluctuate, making your monthly payments unpredictable.
- Fixed Interest Rates: Fixed interest rates remain constant for the duration of the loan, providing predictability and stability in your payments. However, if interest rates fall significantly after securing a fixed-rate loan, you might miss out on potential savings.
- Changing Market Conditions: The economic landscape can change rapidly, affecting your business’s performance and ability to repay your loan. Recessions, industry downturns, or unexpected events can disrupt your revenue streams and make it difficult to meet your financial obligations.
- Industry-Specific Challenges: Certain industries are more susceptible to market fluctuations than others. For example, the tourism and hospitality sectors are highly sensitive to economic downturns and travel restrictions.
- Competition: Increased competition can erode your market share and impact your profitability, making it harder to manage your loan repayments.
Managing Loan Risks
Effectively managing loan risks is crucial for the long-term success of your business. Here are some strategies to mitigate these risks:
- Thorough Financial Planning: Develop a comprehensive financial plan that Artikels your revenue projections, expenses, and cash flow management. This plan should be realistic and consider potential market fluctuations.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Regularly monitor your cash flow to ensure you have sufficient funds to cover your loan payments and other operational expenses.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Create a detailed budget that allocates funds to different areas of your business and forecast your revenue and expenses over a specific period.
- Loan Structure and Terms: Carefully evaluate the loan structure and terms offered by different lenders. Consider factors such as:
- Interest Rates: Compare interest rates from multiple lenders and choose the most favorable option.
- Loan Term: Select a loan term that aligns with your business’s financial projections and repayment capabilities.
- Repayment Schedule: Understand the repayment schedule and ensure it fits your cash flow projections.
- Prepayment Penalties: Inquire about any prepayment penalties that may apply if you decide to pay off the loan early.
- Diversification: Diversify your revenue streams to reduce reliance on a single source of income. This can help cushion your business against unexpected market changes.
- Multiple Products or Services: Offer a range of products or services to cater to different customer segments and market needs.
- Multiple Markets: Expand your operations to new markets or geographic locations to reduce dependence on a single market.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Implement risk mitigation strategies to protect your business from potential threats.
- Insurance: Obtain appropriate insurance coverage to protect your assets and business operations from unforeseen events.
- Contingency Planning: Develop contingency plans to address potential disruptions to your business, such as natural disasters or economic downturns.
Personal Loans vs. Commercial Loans

Choosing the right type of loan for your business needs can be challenging, especially when faced with options like personal loans and commercial loans. While both offer financial assistance, they differ significantly in terms of their features, benefits, and eligibility requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your business goals and financial situation.
Features and Benefits
The key difference between personal and commercial loans lies in their intended purpose. Personal loans are designed for individual needs, such as debt consolidation, home improvement, or medical expenses. In contrast, commercial loans are specifically tailored for business purposes, such as financing equipment, inventory, or working capital. Here’s a table comparing the features and benefits of personal and commercial loans:
| Feature | Personal Loan | Commercial Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Personal expenses | Business expenses |
| Eligibility | Based on individual credit score and income | Based on business credit history, financial statements, and cash flow |
| Interest Rates | Generally higher than commercial loans | Generally lower than personal loans |
| Loan Terms | Shorter terms, typically 1-5 years | Longer terms, typically 5-10 years or more |
| Repayment Options | Fixed monthly payments | Fixed or variable monthly payments, depending on the loan type |
| Collateral | May or may not require collateral | Usually requires collateral, such as equipment or real estate |
| Documentation | Typically requires less documentation | Requires extensive documentation, including financial statements, business plans, and tax returns |
When to Use Each Type of Loan
Choosing between a personal and commercial loan depends on your specific needs and circumstances.
Personal Loans
Personal loans can be a viable option for small business owners with limited credit history or who need a smaller amount of funding for short-term purposes. For example, a sole proprietor might use a personal loan to cover initial operating expenses or purchase equipment.
Commercial Loans
Commercial loans are more suitable for established businesses with a solid credit history and a well-defined business plan. They offer larger loan amounts and longer terms, making them ideal for significant investments, such as expanding operations, purchasing real estate, or financing major equipment purchases.
Key Differences in Terms
Personal and commercial loans also differ in terms of interest rates, loan terms, and repayment options.
Interest Rates
Personal loans typically have higher interest rates than commercial loans. This is because lenders perceive personal loans as riskier due to the lack of business collateral and potential for personal financial instability.
Loan Terms
Commercial loans generally offer longer terms than personal loans, allowing businesses to spread out repayments over a longer period. This can be advantageous for managing cash flow and reducing monthly payment burdens.
Repayment Options
Personal loans usually have fixed monthly payments, while commercial loans may offer both fixed and variable payment options. Variable payment options can fluctuate based on market interest rates, which can impact monthly payments.
Unsecured Loans vs. Commercial Loans
When seeking funding for your new business, understanding the differences between unsecured and commercial loans is crucial. While both options offer financial support, they come with distinct features, benefits, and eligibility requirements. Choosing the right loan type depends on your specific business needs and financial situation.
Features and Benefits
Unsecured loans and commercial loans differ significantly in terms of their features and benefits.
- Unsecured Loans: These loans are not backed by collateral, meaning the lender relies on your creditworthiness for repayment. They are generally easier to obtain than commercial loans, with faster approval times and lower documentation requirements. However, they typically come with higher interest rates and shorter repayment terms.
- Commercial Loans: These loans are secured by collateral, such as equipment, inventory, or real estate. This provides the lender with a safety net in case of default. Commercial loans often offer lower interest rates and longer repayment terms than unsecured loans, making them more attractive for larger investments and long-term growth.
Eligibility Requirements
The eligibility requirements for unsecured and commercial loans vary depending on the lender and the loan amount. However, some common requirements include:
- Unsecured Loans: Good credit history, strong financial statements, and a solid business plan. Some lenders may also require a personal guarantee from the business owner.
- Commercial Loans: Strong credit history, detailed business plan, comprehensive financial statements, and sufficient collateral. Lenders may also require a personal guarantee and proof of sufficient cash flow.
Interest Rates, Loan Terms, and Collateral Requirements
Interest rates, loan terms, and collateral requirements are key factors to consider when comparing unsecured and commercial loans.
- Interest Rates: Unsecured loans typically have higher interest rates than commercial loans due to the increased risk for lenders. Interest rates for commercial loans are often lower because of the collateral backing the loan.
- Loan Terms: Unsecured loans usually have shorter repayment terms than commercial loans, ranging from a few months to a few years. Commercial loans can have repayment terms of up to 10 years or more, depending on the loan amount and purpose.
- Collateral Requirements: Unsecured loans do not require collateral, while commercial loans typically require some form of collateral to secure the loan. The type of collateral required will vary depending on the lender and the loan amount.
When to Choose Each Loan Type
The decision of whether to choose an unsecured or commercial loan depends on your specific business needs and financial situation.
- Unsecured Loans: These loans are suitable for smaller businesses with good credit and a need for short-term financing. They can be helpful for covering operational expenses, inventory purchases, or seasonal cash flow needs.
- Commercial Loans: These loans are suitable for larger businesses with strong credit and a need for long-term financing. They can be helpful for major investments, such as purchasing equipment, expanding operations, or acquiring real estate.
Examples of Unsecured and Commercial Loans
- Unsecured Loans: Business credit cards, lines of credit, and short-term loans from online lenders.
- Commercial Loans: Equipment loans, real estate loans, working capital loans, and SBA loans.
Obtaining a commercial loan for a new business can be challenging, but it’s achievable with the right preparation and strategy. By understanding the requirements, building a strong financial foundation, and choosing the right lender, you can increase your chances of securing the funding you need. Remember, careful planning, meticulous documentation, and a commitment to financial responsibility are key to a successful loan application process.
With a well-crafted business plan, a strong credit history, and a clear understanding of the loan terms, you can confidently approach lenders and secure the financial resources to launch your business and achieve your entrepreneurial goals.
Expert Answers
What is the minimum credit score required for a commercial loan?
There’s no universal minimum credit score requirement, but generally, a score of 680 or higher is considered good for securing a commercial loan. However, lenders often have their own specific criteria, so it’s best to check with them directly.
How long does it take to get a commercial loan approved?
The approval process can vary depending on the lender and the complexity of your application. It can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. It’s essential to start the process early and gather all the necessary documentation.
What happens if my loan application is denied?
If your loan application is denied, the lender will typically provide a reason. It’s important to understand why your application was rejected and work on addressing those concerns. You may need to improve your credit score, strengthen your business plan, or seek alternative financing options.