Investing in commercial real estate can be a lucrative venture, but securing the necessary financing can be a daunting task. Understanding the intricacies of commercial real estate loans is crucial for navigating this complex landscape. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to obtain the funding you need to realize your investment goals.
From understanding the different loan types and eligibility criteria to navigating the application process and managing your loan effectively, we’ll cover all the essential aspects of obtaining a commercial real estate loan. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, this guide will serve as your roadmap to success.
Understanding Commercial Loans for Real Estate Investment
Commercial real estate loans are a specialized type of financing designed to help investors purchase, renovate, or refinance income-producing properties. These loans differ from traditional mortgages in several ways, making it crucial to understand their unique features before applying.
Types of Commercial Real Estate Loans
Commercial real estate loans are categorized based on the type of property being financed, the loan’s purpose, and the borrower’s financial profile. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Construction Loans: These loans are specifically designed to finance the construction of new commercial properties. They typically have shorter terms than permanent loans and require periodic progress payments.
- Bridge Loans: Bridge loans are short-term loans used to bridge the gap between the sale of one property and the purchase of another. They offer flexibility but usually come with higher interest rates.
- Permanent Loans: Permanent loans, also known as long-term loans, are used to finance the purchase or refinancing of existing commercial properties. They typically have fixed interest rates and longer terms than construction or bridge loans.
- Acquisition Loans: These loans are used to finance the purchase of an existing commercial property. They are often used by investors looking to acquire a property for rental income or for business operations.
- Refinancing Loans: Refinancing loans allow borrowers to replace an existing commercial loan with a new loan, often with a lower interest rate or different terms.
Key Features and Benefits of Commercial Real Estate Loans
Commercial real estate loans offer several advantages for investors, including:
- Longer Terms: Compared to personal or unsecured loans, commercial real estate loans typically have longer terms, allowing borrowers to spread out their payments over a longer period.
- Lower Interest Rates: Commercial real estate loans often have lower interest rates than other types of loans, particularly for borrowers with good credit and a strong financial history.
- Flexible Loan Structures: Commercial real estate loans can be tailored to meet the specific needs of borrowers, including varying loan terms, interest rates, and payment schedules.
- Higher Loan Amounts: Commercial real estate loans allow investors to access larger loan amounts, enabling them to finance significant real estate investments.
Comparison with Other Loan Types
Commercial real estate loans differ significantly from other loan types, such as personal loans, unsecured loans, and student loans.
| Loan Type | Purpose | Interest Rates | Loan Amounts | Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Real Estate Loan | Financing income-producing properties | Generally lower | Higher | Longer |
| Personal Loan | Consolidation of debt, home improvement, medical expenses | Higher | Lower | Shorter |
| Unsecured Loan | Debt consolidation, business expenses | Higher | Lower | Shorter |
| Student Loan | Financing education expenses | Variable | Lower | Longer |
Eligibility Criteria for Commercial Real Estate Loans

Securing a commercial real estate loan is a significant step for investors. Lenders carefully assess potential borrowers to ensure their ability to repay the loan. This evaluation process involves various factors, including the borrower’s creditworthiness, the property’s value, and the loan’s purpose.
Credit Score and Financial History
A strong credit score and a solid financial history are crucial for obtaining a commercial real estate loan. Lenders rely on these factors to gauge your financial responsibility and ability to manage debt. A credit score typically reflects your past borrowing and repayment behavior, while financial history encompasses your income, assets, and liabilities.
- A good credit score generally falls within the range of 670 to 740 or higher. A score below 670 could indicate a higher risk for lenders and may lead to a higher interest rate or even loan denial.
- Lenders also review your debt-to-income ratio (DTI), which is the percentage of your monthly income used to pay off existing debts. A lower DTI indicates greater financial flexibility and a lower risk for lenders.
“A strong credit score and a solid financial history are essential for securing favorable loan terms. Lenders view these factors as indicators of your financial responsibility and ability to manage debt.”
Preparing for a Commercial Real Estate Loan Application

To increase your chances of securing a commercial real estate loan, you need to present yourself as a credible borrower. This involves demonstrating your financial strength and the viability of your investment. Here’s how to prepare for a successful application:
Organizing a Detailed Business Plan
A well-structured business plan Artikels your investment strategy and showcases your understanding of the real estate market. It’s a crucial document that lenders use to assess your ability to manage the property and repay the loan.
- Market Analysis: This section should delve into the local real estate market, analyzing trends, supply and demand, and potential growth opportunities. You should include data on property values, vacancy rates, and rental income projections. For example, you could analyze the average rental income for similar properties in the area, and use this data to forecast your potential rental income.
- Investment Strategy: Describe your long-term goals for the property. This could include plans for renovation, expansion, or potential resale. For instance, you could Artikel your strategy for attracting tenants, managing the property, and achieving a specific return on investment.
- Financial Projections: Provide detailed financial projections, including income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. These projections should be realistic and supported by market data. For example, you could project your monthly rental income, operating expenses, and net income over the next few years.
- Exit Strategy: Artikel your plan for eventually exiting the investment. This could include selling the property, refinancing the loan, or holding the property long-term. For instance, you could specify your intended holding period, potential exit scenarios, and the expected return on investment.
Creating a Comprehensive Financial Statement
Lenders want to see that you have the financial resources to manage the property and make loan payments. A comprehensive financial statement demonstrates your financial stability and ability to handle debt.
- Personal Financial Statement: This statement should include your income, assets, liabilities, and net worth. It should reflect your overall financial picture and your ability to service debt. For example, you could include information about your employment history, salary, savings, investments, and outstanding loans.
- Business Financial Statements: If you own a business, provide your company’s financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These documents show the financial health of your business and your ability to repay the loan. For instance, you could include your business’s revenue, expenses, profits, and cash flow for the past few years.
- Tax Returns: Provide copies of your recent tax returns to demonstrate your income history and tax compliance. This information helps lenders assess your financial history and ability to meet your financial obligations. For example, you could provide copies of your income tax returns for the past two to three years.
Preparing a Property Valuation Report
A property valuation report is essential for determining the market value of the property. It provides an objective assessment of the property’s worth, which is crucial for lenders to determine the loan amount and loan-to-value ratio.
- Appraisal: Obtain a professional appraisal from a qualified appraiser. An appraisal provides an independent assessment of the property’s market value, taking into account factors such as location, condition, and comparable sales. For example, an appraiser could consider recent sales of similar properties in the area to determine the property’s fair market value.
- Comparative Market Analysis (CMA): Conduct a CMA to analyze recent sales of similar properties in the area. This analysis helps you understand the current market conditions and estimate the property’s potential value. For instance, you could analyze recent sales of properties with similar features, location, and condition to determine the property’s potential selling price.
- Property Condition Assessment: If the property requires repairs or renovations, consider obtaining a property condition assessment report. This report identifies any potential issues that could affect the property’s value or require additional expenses. For example, a property condition assessment could identify structural defects, plumbing issues, or electrical problems that need to be addressed.
Finding the Right Lender for Your Needs
Securing the right lender is crucial for your commercial real estate investment success. The loan terms, interest rates, and lender’s reputation can significantly impact your project’s financial viability. Finding the right lender involves understanding the various types of lenders, comparing their offerings, and meticulously researching their reputation. This section delves into these aspects to guide you in making an informed decision.
Types of Commercial Real Estate Lenders
There are various types of lenders offering commercial real estate loans, each with its own set of terms, interest rates, and requirements. Here’s a breakdown of common lenders:
- Banks: Traditional banks are often the first choice for commercial real estate loans. They typically offer competitive interest rates and flexible loan terms, especially for borrowers with good credit history and substantial collateral.
- Credit Unions: Credit unions are member-owned financial institutions known for their personalized service and competitive rates. They may be a good option for borrowers who are part of a specific community or industry.
- Private Lenders: Private lenders, such as hedge funds and investment firms, provide financing for projects that might not qualify for traditional loans. They often have higher interest rates and stricter requirements but can offer faster funding and more flexibility in loan terms.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): REITs are companies that invest in and manage commercial real estate properties. Some REITs offer financing to developers and investors.
- Online Lenders: Online lenders are gaining popularity for their streamlined application process and faster funding times. They often have more flexible requirements than traditional banks but may charge higher interest rates.
Comparing Loan Terms and Interest Rates
Once you’ve identified potential lenders, carefully compare their loan terms and interest rates. Key factors to consider include:
- Interest Rate: This is the cost of borrowing money. Interest rates can vary depending on the lender, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and the type of loan.
- Loan Term: The loan term is the duration of the loan. Longer loan terms generally result in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest costs.
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: The LTV ratio is the percentage of the property’s value that the lender is willing to finance. A higher LTV ratio means a larger loan amount but may require a higher interest rate.
- Fees: Lenders may charge various fees, such as origination fees, closing costs, and appraisal fees.
- Prepayment Penalties: Some lenders may charge a penalty if you pay off the loan early.
Researching and Selecting a Reputable Lender
It’s crucial to choose a lender with a solid reputation and proven track record. Here’s how to conduct thorough research:
- Check Online Reviews: Look for reviews from past clients on websites like Yelp, Google Reviews, and Trustpilot.
- Read Industry Publications: Publications like The Real Estate Journal and Commercial Property Executive often feature rankings and reviews of lenders.
- Talk to Other Investors: Ask other real estate investors for recommendations.
- Contact the Better Business Bureau (BBB): The BBB provides information about businesses and their customer complaints.
Tip: Don’t hesitate to ask for references from the lender. This allows you to talk to previous clients and get firsthand insights into their experience.
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
Before diving into the exciting world of real estate investment, it’s crucial to understand the intricacies of commercial loan terms and conditions. These terms define the financial framework of your loan, influencing your investment’s success.
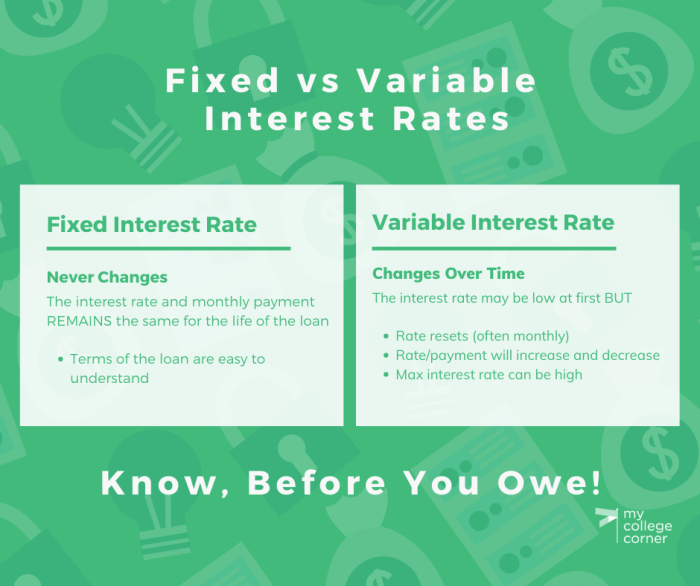
Interest Rates
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money. Understanding how interest rates affect your loan payments is essential. Here’s a breakdown:
- Fixed Interest Rates: These rates remain constant throughout the loan term, providing predictability in your monthly payments. This stability is advantageous in a fluctuating market, ensuring consistent budgeting.
- Variable Interest Rates: These rates fluctuate based on market conditions. While initially lower than fixed rates, they can increase over time, potentially impacting your budget. However, variable rates offer potential savings if market rates decline.
Loan Periods
The loan period, also known as the amortization period, dictates the length of time you have to repay the loan. This duration significantly impacts your monthly payments and the overall cost of borrowing.
- Shorter Loan Periods: Lead to higher monthly payments but result in lower overall interest costs. This option is ideal for investors seeking to minimize long-term debt obligations.
- Longer Loan Periods: Offer lower monthly payments but incur higher overall interest costs. This option can be attractive for investors aiming for lower upfront financial commitments.
Repayment Schedules
Repayment schedules Artikel the frequency and amount of your loan payments. Understanding these schedules is crucial for managing your cash flow.
- Amortized Loans: These loans involve regular payments that cover both principal and interest. The principal amount gradually decreases over time, while the interest portion declines as the loan progresses.
- Interest-Only Loans: These loans require only interest payments during the loan term, with the principal amount repaid in a lump sum at maturity. This option provides flexibility for investors who anticipate generating sufficient income to cover the principal payment at the end of the loan term.
Loan Fees
Commercial loans often come with various fees, including:
- Origination Fees: These fees are charged by the lender to cover the costs associated with processing your loan application. Typically calculated as a percentage of the loan amount.
- Closing Costs: These fees cover expenses related to the closing of the loan, including appraisal fees, title insurance, and legal fees.
Loan Covenants
Loan covenants are specific terms and conditions Artikeld in the loan agreement that dictate the borrower’s responsibilities and obligations. These covenants aim to protect the lender’s interests and ensure responsible financial management.
- Financial Covenants: These covenants set limits on the borrower’s financial performance, such as debt-to-equity ratios and operating margins. They ensure that the borrower maintains financial stability and can meet its loan obligations.
- Operational Covenants: These covenants govern the borrower’s business operations, including restrictions on asset sales, dividend payments, and acquisitions. They aim to maintain the value of the investment property and protect the lender’s interests.
Negotiating Favorable Loan Terms
Negotiating favorable loan terms is crucial to securing a loan that aligns with your investment goals.
- Shop Around: Comparing offers from multiple lenders allows you to identify the most competitive interest rates, loan fees, and terms.
- Strong Credit History: A strong credit score enhances your negotiating power, as lenders view you as a low-risk borrower. This often translates into more favorable interest rates and terms.
- Solid Business Plan: A well-structured business plan demonstrating the viability of your investment project can sway lenders to offer more favorable terms.
- Negotiate Flexibility: Be prepared to negotiate on various loan terms, such as interest rates, loan periods, and fees. Don’t be afraid to request concessions to secure the most favorable deal.
Securing a commercial real estate loan requires meticulous planning, a strong financial foundation, and a thorough understanding of the loan process. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can increase your chances of obtaining the financing you need to invest in profitable commercial real estate properties. Remember, careful research, effective communication, and a proactive approach are key to navigating this journey successfully.
Helpful Answers
What are the typical interest rates for commercial real estate loans?
Interest rates for commercial real estate loans vary depending on factors like loan type, property type, borrower creditworthiness, and prevailing market conditions. They are generally higher than residential mortgage rates.
How long does it typically take to get a commercial real estate loan approved?
The loan approval process can take several weeks to months, depending on the complexity of the loan and the lender’s underwriting procedures.
What are the common reasons for commercial real estate loan denials?
Common reasons for loan denials include poor credit history, insufficient income, inadequate collateral, or a weak business plan.