Refinancing a personal loan can be a smart move to lower your monthly payments and save money in the long run. But with so many lenders and options, it can feel overwhelming to know where to start. This guide will walk you through the steps of refinancing, from understanding your eligibility to choosing the right lender and navigating the application process.
We’ll also explore alternative debt consolidation strategies and discuss key loan types to help you make informed decisions about your finances.
Whether you’re looking to consolidate high-interest debt, take advantage of lower rates, or simply free up some cash flow, refinancing can be a valuable tool. By following these steps, you can streamline the process and increase your chances of securing a favorable loan.
Understanding Refinancing

Refinancing a personal loan means getting a new loan to pay off your existing one. This can be beneficial if you can secure a lower interest rate, which could lead to lower monthly payments. By refinancing, you essentially replace your old loan with a new one, potentially getting a better deal in the process.
Benefits of Refinancing
Refinancing can offer several advantages, making it a worthwhile consideration for many borrowers.
- Lower Monthly Payments: This is often the primary motivation for refinancing. By securing a lower interest rate, you can reduce the amount of interest you pay over the life of the loan, resulting in lower monthly payments. This can free up more cash in your budget for other financial goals.
- Shorter Loan Term: While a shorter loan term usually means higher monthly payments, it can be beneficial in the long run. You’ll pay off the loan faster, saving on interest charges and potentially increasing your credit score.
- Consolidation of Debt: If you have multiple personal loans with different interest rates, refinancing can consolidate them into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This can simplify your debt management and potentially lower your overall interest costs.
- Improved Credit Score: If you’ve improved your credit score since taking out your original loan, you may qualify for a lower interest rate when refinancing. This can lead to lower monthly payments and potentially save you money in the long run.
Drawbacks of Refinancing
While refinancing can be beneficial, it’s essential to consider the potential drawbacks before making a decision.
- Origination Fees: Lenders may charge an origination fee for processing your refinancing application. This fee can be a percentage of the loan amount, so it’s important to factor it into your overall costs.
- Closing Costs: Similar to origination fees, closing costs can include various expenses, such as appraisal fees, title insurance, and recording fees. These costs can add up, so it’s crucial to understand them before proceeding.
- Prepayment Penalties: Some loans may include prepayment penalties, which discourage borrowers from paying off the loan early. If you’re considering refinancing, ensure your existing loan doesn’t have a prepayment penalty, as it could offset the benefits of refinancing.
- Increased Loan Term: While a shorter loan term is often desirable, refinancing might sometimes involve a longer loan term. This can result in paying more interest over the life of the loan, even if your monthly payments are lower.
Scenarios Where Refinancing Might Be Advantageous
Refinancing can be a wise choice in various situations, but it’s crucial to carefully assess your circumstances.
- Lower Interest Rates: If interest rates have dropped since you took out your personal loan, refinancing can potentially save you money on interest charges.
- Improved Credit Score: If you’ve improved your credit score since taking out your loan, you may qualify for a lower interest rate, making refinancing beneficial.
- Consolidation of Debt: If you have multiple personal loans with different interest rates, refinancing can help you consolidate them into a single loan with a lower interest rate, simplifying your debt management.
- Financial Hardship: If you’re facing financial hardship, refinancing your loan with a longer term can lower your monthly payments, making it easier to manage your finances.
Applying for Refinancing
Once you’ve decided to refinance your personal loan, it’s time to apply. The application process is similar to applying for the original loan, but with a few key differences. You’ll need to gather your financial documents, such as your income verification, credit report, and bank statements.
Submitting a Refinancing Application
To submit a refinancing application, you’ll need to follow these steps:
- Choose a lender. Compare interest rates, fees, and terms from multiple lenders to find the best option for your needs.
- Gather your documents. You’ll need to provide the lender with your income verification, credit report, and bank statements.
- Complete the application. This will typically involve providing your personal information, loan details, and financial information.
- Submit your application. Once you’ve completed the application, you can submit it electronically or by mail.
Reviewing the Loan Agreement
After submitting your application, the lender will review it and make a decision. If your application is approved, you’ll receive a loan agreement. It’s crucial to review this agreement carefully before signing.
Important: Make sure you understand the terms and conditions of the loan, including the interest rate, fees, and repayment schedule. If you’re unsure about anything, don’t hesitate to ask the lender for clarification.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
During the application process, you may encounter some challenges. Here are a few common challenges and solutions:
- Your credit score may be too low. If your credit score is low, you may be denied refinancing or offered a higher interest rate. To improve your credit score, you can pay your bills on time, reduce your credit card debt, and avoid opening new accounts.
- You may not have enough income. Lenders will typically require a certain level of income to qualify for refinancing. If you don’t meet the income requirements, you may need to find a cosigner or look for a lender with more flexible requirements.
- The lender may not offer the terms you’re looking for. If the lender doesn’t offer the interest rate or repayment terms you want, you may need to shop around for a different lender.
Understanding Loan Terms

When you refinance a personal loan, you’re essentially taking out a new loan to pay off your existing one. Understanding the key terms of your new loan is crucial to making sure you’re getting a good deal and achieving your refinancing goals.
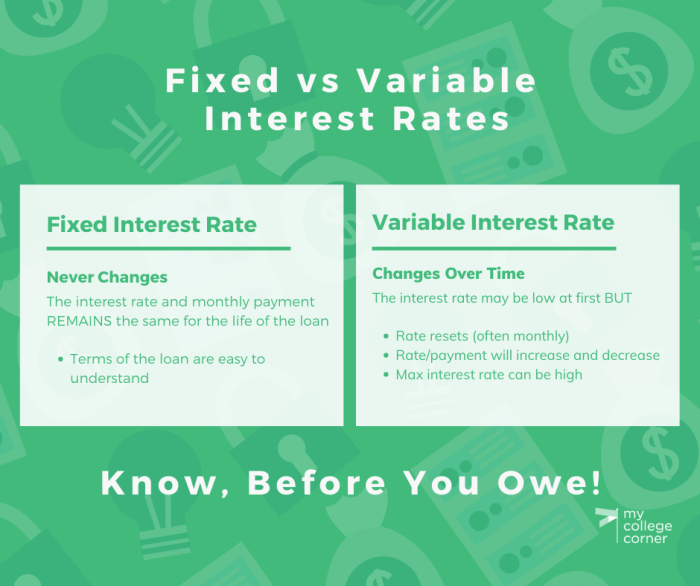
Interest Rate
The interest rate is the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the loan amount. A lower interest rate will result in lower monthly payments and a lower overall cost of borrowing. A higher interest rate will result in higher monthly payments and a higher overall cost of borrowing.
Loan Term
The loan term is the length of time you have to repay the loan. A longer loan term will result in lower monthly payments, but you’ll end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan. A shorter loan term will result in higher monthly payments, but you’ll pay less in interest overall.
Repayment Schedule
The repayment schedule Artikels how much you’ll need to pay each month and when those payments are due. Most personal loans have fixed monthly payments, but some may offer flexible repayment options.
Impact of Loan Terms
The combination of your interest rate, loan term, and repayment schedule will determine your monthly payments and the total cost of your loan.
For example, let’s say you have a $10,000 personal loan with a 10% interest rate and a 5-year term. Your monthly payment would be $212.47, and you would pay a total of $12,748.20 over the life of the loan. If you were to refinance that loan with a 7% interest rate and a 4-year term, your monthly payment would be $240.54, but you would pay a total of $11,545.92 over the life of the loan.
Negotiating Favorable Loan Terms
You may be able to negotiate more favorable loan terms, such as a lower interest rate or a shorter loan term. Here are some tips for negotiating:
- Shop around for loans from multiple lenders.
- Have a good credit score.
- Be prepared to make a larger down payment.
- Be willing to walk away if you don’t get a good deal.
Managing Your Refinanced Loan
You’ve successfully refinanced your personal loan and secured a lower monthly payment. Now, it’s crucial to manage your refinanced loan effectively to reap the benefits of lower interest rates and ensure a smooth repayment journey.
Budgeting and Timely Payments
Budgeting is essential for managing your refinanced loan effectively. By creating a realistic budget, you can allocate funds for your loan payments and avoid missing deadlines. Here are some tips for budgeting:
- Track your income and expenses.
- Identify areas where you can cut back on spending.
- Set up automatic payments to ensure timely repayments.
Monitoring Your Credit Score
Maintaining a good credit score is crucial for securing favorable loan terms and interest rates in the future. Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, reflecting your ability to repay borrowed funds. A higher credit score signifies a lower risk for lenders, resulting in better loan terms. Here are some tips for monitoring your credit score:
- Check your credit report regularly.
- Dispute any errors or inaccuracies on your credit report.
- Make timely payments on all your debts.
Avoiding Late Fees and Penalties
Late payments can significantly impact your credit score and lead to hefty penalties. These penalties can erode the benefits of refinancing and add to your overall debt burden. Here are some strategies for avoiding late fees and penalties:
- Set reminders for your loan payment due dates.
- Consider setting up automatic payments to ensure timely repayments.
- Communicate with your lender if you anticipate a late payment.
Exploring Alternatives
Refinancing your personal loan isn’t the only way to reduce your monthly payments or consolidate your debt. Several other options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. It’s crucial to carefully consider your financial situation and goals before choosing the best path.
Comparing Refinancing with Other Debt Consolidation Options
There are several alternatives to refinancing your personal loan for debt consolidation, each with its own set of pros and cons:
- Balance Transfers: Transferring your existing credit card balances to a new card with a lower interest rate can be a cost-effective way to reduce interest payments. This strategy works best when you can pay off the transferred balance before the introductory period ends, as interest rates usually rise after that point.
- Debt Management Programs: These programs, often offered by non-profit credit counseling agencies, help you manage your debt by negotiating lower interest rates and monthly payments with your creditors. While they can be helpful, these programs typically require a monthly fee and may affect your credit score.
Balance Transfers
Balance transfers offer a way to consolidate credit card debt by moving it to a new card with a lower interest rate.
- Pros:
- Lower Interest Rates: Transferring your balance to a card with a lower interest rate can save you money on interest charges.
- Introductory Periods: Many balance transfer cards offer introductory periods with 0% interest, giving you time to pay off the balance without accruing interest.
- Convenience: Combining multiple credit card balances into one can simplify your debt management.
- Cons:
- Balance Transfer Fees: Most cards charge a fee for transferring your balance, usually a percentage of the transferred amount.
- Limited Timeframe: Introductory periods with 0% interest typically last for a limited time, usually 12 to 18 months. After the introductory period ends, the interest rate on the balance transfer card will revert to its standard rate, which can be significantly higher.
- Credit Score Impact: Applying for a new credit card can temporarily lower your credit score, especially if you already have several open credit accounts.
Debt Management Programs
Debt management programs, often offered by non-profit credit counseling agencies, provide a structured approach to managing your debt.
- Pros:
- Lower Interest Rates: Debt management programs often negotiate lower interest rates and monthly payments with your creditors.
- Financial Counseling: Credit counseling agencies provide guidance and support to help you manage your finances and develop a budget.
- Protection from Collection Calls: Debt management programs can help protect you from harassment by creditors.
- Cons:
- Fees: Debt management programs typically charge a monthly fee for their services.
- Credit Score Impact: Debt management programs may negatively impact your credit score, as they often involve opening a new credit account.
- Long-Term Commitment: Debt management programs can take several years to complete, requiring a significant commitment.
Related Loan Types
Understanding different loan types can help you determine the best option for your specific financial needs. It’s essential to understand the differences and similarities between various loans to make informed decisions about borrowing.
Personal Loans
Personal loans are versatile and can be used for various purposes, such as debt consolidation, home improvements, medical expenses, or even vacations. They are typically unsecured loans, meaning they don’t require collateral. This makes them easier to obtain but can also result in higher interest rates.
Unsecured Loans
Unsecured loans, like personal loans, are not backed by any collateral. This means the lender relies on your creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan. Examples of unsecured loans include personal loans, credit cards, and payday loans. They are often associated with higher interest rates than secured loans because the lender bears more risk.
Commercial Loans
Commercial loans are designed for businesses and are used for various purposes, such as purchasing equipment, expanding operations, or managing cash flow. These loans can be secured or unsecured, depending on the lender’s requirements and the borrower’s financial situation. Commercial loans typically involve larger loan amounts and longer repayment terms than personal loans.
Student Loans
Student loans are specifically designed to help students finance their education. They can be federal or private, and they offer different interest rates and repayment terms. Federal student loans often have lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options than private student loans. Student loans are typically unsecured, meaning they don’t require collateral.
Refinancing a personal loan can be a complex process, but by understanding your options, carefully evaluating your eligibility, and choosing the right lender, you can potentially save money and improve your financial situation. Remember to review the loan agreement thoroughly before signing, and always prioritize responsible financial management to ensure long-term success.
FAQ Section
How does refinancing a personal loan work?
Refinancing involves taking out a new loan to pay off your existing personal loan. The new loan typically has a lower interest rate, which results in lower monthly payments and potentially lower overall interest charges.
What are the potential drawbacks of refinancing?
While refinancing can be beneficial, there are potential drawbacks. For example, you may incur origination fees or closing costs, and the new loan may have a longer term, which could increase the total amount of interest paid over the life of the loan.
Can I refinance my personal loan if I have a low credit score?
Lenders typically prefer borrowers with good credit scores. However, you may still be able to refinance with a lower credit score, but you may receive a higher interest rate or face stricter terms.
What documents do I need to refinance my personal loan?
The required documents will vary depending on the lender, but typically include your Social Security number, income verification, bank statements, and proof of residency.
How long does it take to refinance a personal loan?
The refinancing process can take several weeks or even months, depending on the lender and the complexity of your application.